Amid the global shift toward sustainable business practices, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives have become a bedrock for modern corporate strategies. With new regulations such as the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the U.S. SEC’s proposed rule on climate disclosures, coupled with increased stakeholder demands for accountability, companies find themselves navigating a complex landscape where the accuracy and transparency of ESG data takes center stage. From compliance obligations to strategic initiatives, the journey toward building trust with stakeholders is tied to a well-developed system of internal controls.
In this blog, we’ll explore the critical role of internal controls for ESG data and reporting—unveiling the benefits, challenges, and essential steps for implementation.
What are internal controls?
Internal controls, commonly associated with financial management, are systematic procedures and practices implemented by an organization to safeguard assets, ensure accuracy in reporting, and enhance operational efficiency. Common controls such as segregation of duties, approval thresholds, and data verifications serve as a set of checks and balances, mitigating the risk of errors, frauds, and non-compliance.
Beyond their traditional application in finance, internal controls play an increasingly integral role in ESG data. As companies strive to meet sustainability goals and address stakeholder expectations, robust internal controls are essential for validating the accuracy and reliability of data, fostering transparency, and building trust in the broader context of responsible business practices.
Understanding ESG data and reporting
ESG criteria have become essential tools for investors, analysts, and a broad spectrum of stakeholders seeking to evaluate a company’s dedication to sustainable and ethical practices. ESG reporting involves disclosing information on a company’s performance within the three pillars—environmental, social, and governance—providing stakeholders with insight into its sustainability practices. As ESG considerations continue to gain prominence in investment decisions and corporate governance, the accuracy of data is crucial for building credibility and trust.
Stakeholders play a pivotal role in utilizing ESG data and reporting to inform their decision-making processes and influence corporate behavior. Here’s a closer look at how different stakeholders leverage this information:
- Investors and Analysts: Investors and analysts integrate ESG criteria into their strategies for insights into a company’s sustainability and risk exposure. This data is used to evaluate a company’s overall performance, resilience to external shocks, regulatory compliance, and potential for long-term growth. Additionally, it aids in identifying ethical opportunities, assessing ESG risks, and attracting socially responsible investors.
- Customers and Consumers: Consumers use ESG data to make informed decisions that align with their values. Companies with strong ESG profiles gain a competitive edge by attracting and retaining customers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices.
- Employees: 71% of job seekers under 35 and 58% of all job seekers factor in a company’s commitment to sustainability when choosing an employer. ESG data provides insight into a company’s commitment to social responsibility, diversity, and ethical governance, influencing employee satisfaction, workplace culture, and talent attraction and retention.
- Regulators and Policymakers: Regulators use ESG data to assess a company’s compliance with regulations, labor standards, and governance requirements. This information aids in policy development and supports adjustments to regulatory frameworks.
- Suppliers and Business Partners: In order to better understand their broader impacts and meet their own ESG goals, companies with ESG commitments assess the performance of suppliers and partners within their value chains. A commitment to sustainability may be a critical factor in supplier selection, with ESG data enabling evaluations of overall business impact and alignment with values.
- NGOs and Advocacy Groups: NGOs use ESG data to hold companies accountable for social and environmental impacts. Credible information empowers advocacy groups to push for transparency and encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices.
- Local Communities: Local communities use ESG data to assess a company’s impact on the environment, employment practices, and community engagement. This information empowers communities and businesses to engage in constructive dialogues and make positive changes.
When stakeholders rely on ESG data to make critical decisions, the consequences of inaccurate or false information can be profound—and are increasingly leading to legal action and lawsuits. The stakes are high with stakeholders prioritizing transparency and authenticity in sustainability practices. As a result, companies that report inaccurate data or fall short of their stated ESG commitments risk not only legal actions, but severe reputational damage that can have enduring impacts on their standing in the market and relationships with key stakeholders.
The benefits of internal controls in ESG
As stakeholders increasingly rely on ESG data and demand transparency, incorporating internal controls into ESG compliance and strategy becomes vital. Integrating internal controls helps maintain data accuracy and reliability and facilitates adaptation to evolving regulatory standards, positioning companies for compliance and resilience in the face of future changes.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Internal controls are mechanisms that ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial and non-financial data. For ESG reporting, precision is paramount. Implementing internal controls helps companies validate their data, mitigating the risk of errors or inaccuracies that could result in misleading information.
- Stakeholder Trust: Trust is a cornerstone of sustainable business practices. As investors, customers, and other stakeholders demand greater transparency, companies with reliable internal controls for ESG data demonstrate their commitment to accuracy and accountability. This, in turn, builds trust and enhances the company’s reputation in the marketplace.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: The regulatory landscape surrounding ESG reporting is evolving. Many jurisdictions are introducing or considering mandatory ESG disclosure requirements. Establishing internal controls ensures that companies are not only meeting current compliance standards but are also well-prepared for future regulatory changes.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Accurate ESG data empowers companies to make informed strategic decisions. Whether it’s identifying areas for improvement, setting ambitious sustainability goals, or aligning business practices with emerging ESG trends, internal controls provide the foundation for data-driven decision-making.
- Cost of Capital and Access to Funding: Investors increasingly consider ESG factors when making investment decisions. Companies with robust ESG practices and reliable reporting mechanisms may enjoy a lower cost of capital and better access to funding. Internal controls contribute to the confidence investors place in a company’s ESG disclosures.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that prioritize internal controls for ESG data gain a competitive edge by developing a solid reputation for accurate and transparent reporting. This can attract environmentally and socially conscious investors, customers, and partners by differentiating themselves within the market.
- Risk Management: ESG risks, including environmental disasters, supply chain disruptions, or social controversies, can have a profound impact on a company’s value. Internal controls can help identify, assess, and manage these risks by ensuring that the company’s ESG data and processes are accurate, up-to-date, and reflective of its risk exposure.
Challenges in implementing internal controls for ESG
While the benefits of internal controls for ESG are clear, companies may encounter challenges during the implementation process. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the effective establishment and maintenance of internal controls.
- Data Complexity: ESG data can be complex and often involves multiple metrics and indicators to give a full view of the necessary information. Companies may struggle to manage the diverse range of data required for comprehensive ESG reporting. Implementing internal controls that streamline data collection, validation, and reporting processes can help mitigate this challenge.
- Data Quality and Consistency: Maintaining data quality and consistency across multiple business units, departments, and along value chain operations can be challenging. Standardizing data collection methods and investing in technologies that facilitate data governance can enhance the reliability of ESG data.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating ESG data controls within existing internal control systems can be complicated, especially if those systems are designed primarily for financial reporting. Companies need to assess their existing controls and, if necessary, adapt or extend them to accommodate ESG-specific topics.
- Human Capital: Internal controls for ESG require having a workforce with the skills and knowledge to navigate the complexities of sustainability reporting. Companies may need to invest in training and development programs that ensure their teams can effectively implement and manage ESG data controls, or hire an outside expert to guide development and training.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Sustainability is an evolving field, with ESG requirements, expectations, and reporting standards changing over time. Establishing internal controls is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Companies should be agile and adaptable to changes in the ESG landscape.
Implementing internal controls for ESG data
Planning for and establishing internal controls should be a thoughtful and holistic process. It begins with a careful analysis of your company’s ESG risks and drivers, and it involves the input of diverse stakeholders throughout your business.
Contextual analysis: Defining risk and materiality
✓ Assess ESG Regulatory Exposure: Begin by assessing which ESG regulations apply to your business. This helps to provide a foundational understanding of the specific requirements and expectations the company is facing within the evolving regulatory landscape and ensures a proactive approach to compliance and resilience in the face of changing standards.
✓ Conduct a Materiality Assessment: Identify the ESG issues that are most material to your business, considering financial materiality and/or impact materiality based on regulatory requirements. Streamline internal controls to focus on these material ESG aspects, ensuring targeted and effective approach to address the most critical concerns for both your business and stakeholders.
Optimizing data systems
✓ Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish clear and measurable KPIs for each material ESG aspect. These KPIs will serve as the basis for data collection and reporting. Ensure that the selected indicators align with industry standards, stakeholder expectations, and regulatory requirements.
✓ Standardize Data Collection Processes: Standardization is essential for ensuring data quality and consistency. Develop standardized processes for collecting ESG data across business units, divisions, and geographical locations. This includes defining methodologies, units of measurement, and reporting frequencies.
✓ Invest in Technology Solutions: Leveraging technology to streamline data collection, validation, and reporting processes can be a game-changer for internal controls. ESG management software and data analytics tools can enhance efficiency and accuracy while providing a centralized platform for managing ESG data.
Setting a solid foundation
✓ Implement Data Governance Practices: Establish strong data governance practices to ensure data quality and integrity. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for data management, implementing data validation checks, and establishing data quality assurance processes.
✓ Integrate ESG Controls with Existing Systems: Evaluate existing internal control systems and determine how they can be adapted or extended to accommodate ESG-specific controls. Integration is key to ensuring that ESG data controls are seamlessly woven into the broader framework of internal governance.
✓ Engage Stakeholders: Foster a culture of transparency and engagement by involving stakeholders in the ESG reporting process. Solicit feedback, address concerns, and communicate progress. Engaging with stakeholders ensures that your ESG reporting aligns with their expectations and needs.
Aiming for continuous improvement
✓ Provide Training and Raise Awareness: Invest in training programs to enhance the ESG literacy of your workforce. Ensure that employees involved in data collection and reporting understand the importance of ESG controls and their role in maintaining accurate and reliable data.
✓ Establish Continuous Monitoring Mechanisms: Implement continuous monitoring mechanisms to track changes in ESG data and promptly identify discrepancies or anomalies. Regularly review and update internal controls to align with evolving ESG standards and expectations.
✓ Seek External Assurance: Consider obtaining external assurance for your ESG data. External audits or third-party assessments provide an additional layer of credibility, assuring stakeholders that your ESG reporting is accurate, reliable, and aligned with industry best practices.
The below table provides examples of what an internal control could look like within each pillar of ESG. Please note that internal controls are designed based on the specific material risks and business processes identified within a unique organization. The following examples are based on generalized risks and may not be sufficient on their own to reasonably ensure data integrity.
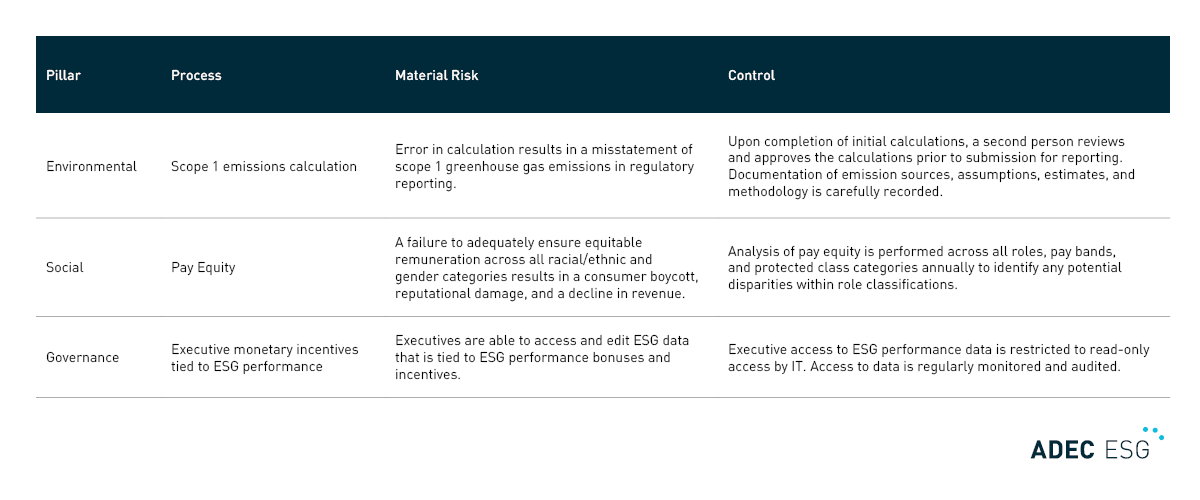
The implementation of internal controls for ESG data and reporting is not only a compliance necessity, but also a strategic imperative for companies wanting to thrive in a sustainable future. By ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and transparency of their ESG disclosures, organizations can build trust among stakeholders, enhance their competitive advantage, and contribute to a more sustainable global economy. The journey towards effective ESG internal controls requires a commitment to continuous improvement, technology adoption, and a culture of accountability. As companies navigate this path, they are not only securing their own future but also contributing to a more resilient and responsible business ecosystem.
ADEC ESG Solutions provides fully-integrated industry expertise, software solutions, and data management to organizations leading global, sustainable change. Sign up for our monthly newsletter GreenWatch to get the latest in ESG sent straight to your inbox, including webinars, industry updates, white papers, and articles like these.




